
- PROCESS MONITOR LINUX HOW TO
- PROCESS MONITOR LINUX INSTALL
- PROCESS MONITOR LINUX SOFTWARE
- PROCESS MONITOR LINUX CODE
To view all listening processes enter the following.
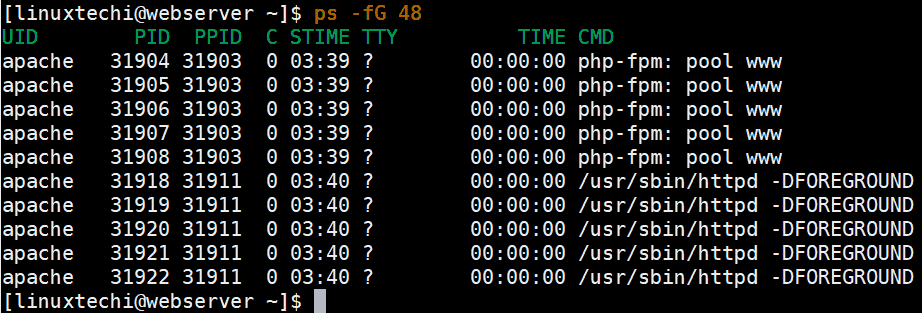
Ss also has a -e option to view extended information, but that option has been omitted from the examples below because it produces additional information that may result in less readable output.
PROCESS MONITOR LINUX HOW TO
Let’s see how to accomplish the same actions as performed above using ss. The netstat command has long been a favorite of sysadmins, however it has recently been replaced by the ss command which boasts of being faster, easier, and more human readable than netstat. If this sparked your interest in netstat then we have an article you can read to Learn more about using the netstat command ss Navigating to the urls for these 2 app badges individually and issuing the above netstat command does indeed verify that they are hosted on servers owned by Google and Akamai respectively.

PROCESS MONITOR LINUX CODE
In fact, examining the source code of the wikipedia homepage reveals that it loads the Google Play Store app-badge from and the Apple AppStore app-badge from. This makes sense considering Wikimedia owns and hosts wikipedia and it is very common for sites to load resources that are hosted on servers owned by Google and Akamai. $ whois 91.198.174.192| lessĭoing so for each of them reveals that they belong to Wikimedia, Google, Google, and Akamai respectively. To see who these servers belong to we can query the ip addresses with whois like so. We entered the above command after navigating to in firefox and the screenshot captures the connections established by firefox when reaching the site. Sudo netstat -atupen | grep ESTABLISHED output To do this enter the following command, which is similar to the previous one except that we use -a to view all sockets instead of -l to just view listening sockets. Now let’s take a look at all of the current network connections. The same distinction is true for tcp6/ udp6 when comparing a Local Address of ::(network facing) and ::1(localhost only). For tcp4/ udp4 connections(simply listed as tcp and udp) where the Local Address is listed as 0.0.0.0 the process is listening for connections from any machine that is able to connect to it over the network, whereas when it is listed as 127.0.0.1 it is only listening for connections on the localhost(the machine that it is running on or itself) and cannot be connected to by other computers on the network. There is one important distinction to note here.
PROCESS MONITOR LINUX INSTALL
These are all of the processes that you would expect to be listening for network connections on a fresh install of RHEL 8 running in VirtualBox.įor each listening process you can see the protocol being used, local address and port it is listening on, the user it is running under, and the PID/Program name.

There is nothing surprising about the output given our setup.
PROCESS MONITOR LINUX SOFTWARE
When considering the client server model that most networking software is based on, listening processes can be thought of as software that is in “server” mode. On Red Hat Enterprise Linux and Red Hat based systems, use yum, # yum install net-tools On Debian and Debian based systems such as Ubuntu, use apt. We will be using it to accomplish the former. Netstat is a powerful utility that can print network connections, routing tables, interface statistics, masquerade connections, and multicast memberships. $ – requires given linux commands to be executed as a regular non-privileged user # – requires given linux commands to be executed with root privileges either directly as a root user or by use of sudo command Privileged access to your Linux system as root or via the sudo command. Netstat, lsof, ifconfig, wireshark, tcpdump
Requirements, Conventions or Software Version Used How to monitor network activity on a Linux system Software requirements and conventions used Software Requirements and Linux Command Line Conventions Category


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
